Web crawlers, sometimes called spiders or bots, are how search engines explore the internet. They crawl billions of pages by following links from one page to the next, similar to how you might click a link to navigate to a new website. This process discovers new pages across the web.
Understanding how search engines work is the foundation of effective SEO. After all, you can’t optimize your website without knowing the system behind it. In this guide, you’ll discover exactly how search engines operate and what makes them tick.
Let’s start by uncovering what search engines truly are, why they were created, and how they generate revenue.
What Are Search Engines?
Search engines are vast, searchable databases that organize the endless content available on the web. They operate through two core components:
-
Search Index: Think of it as a massive digital library that stores information about billions of webpages.
-
Search Algorithm(s): These are intelligent computer programs that analyze the search index and deliver the most relevant results to a user’s query.
What Is the Aim of Search Engines?
At their core, all search engines share a single goal — to deliver the most accurate, relevant, and high-quality results for every user query. The better they meet this goal, the more people trust and use them — which ultimately helps them grow their market share.
How Do Search Engines Make Money?
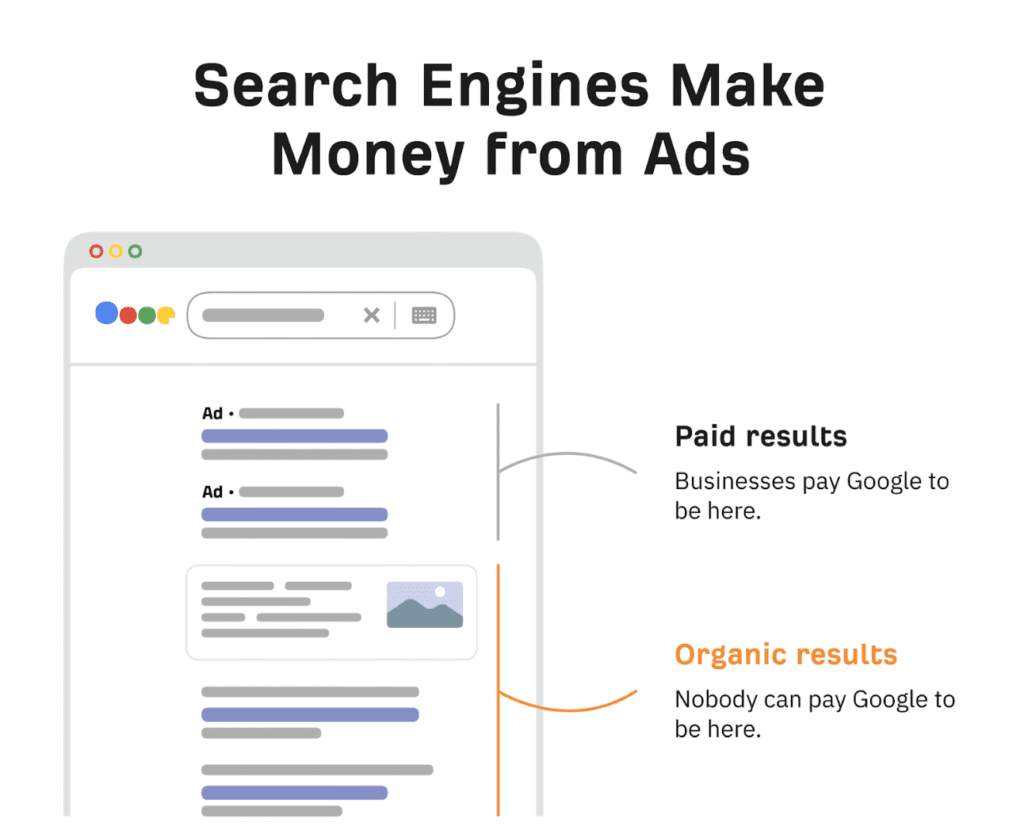
Search engines display two primary types of results:
-
Organic Results: These come directly from the search index and are ranked based on relevance and quality. You cannot pay to appear here.
-
Paid Results: These are advertisements purchased by businesses. Whenever a user clicks on a paid ad, the advertiser pays the search engine — a model known as Pay-Per-Click (PPC) advertising.
This is why market share matters so much. The more people use a search engine, the more ad clicks it receives — and that translates into higher revenue.
Part 2: How Search Engines Build Their Indexes
Every search engine has its own system for creating a search index, but let’s look at a simplified version of how Google — the world’s most popular search engine — does it.
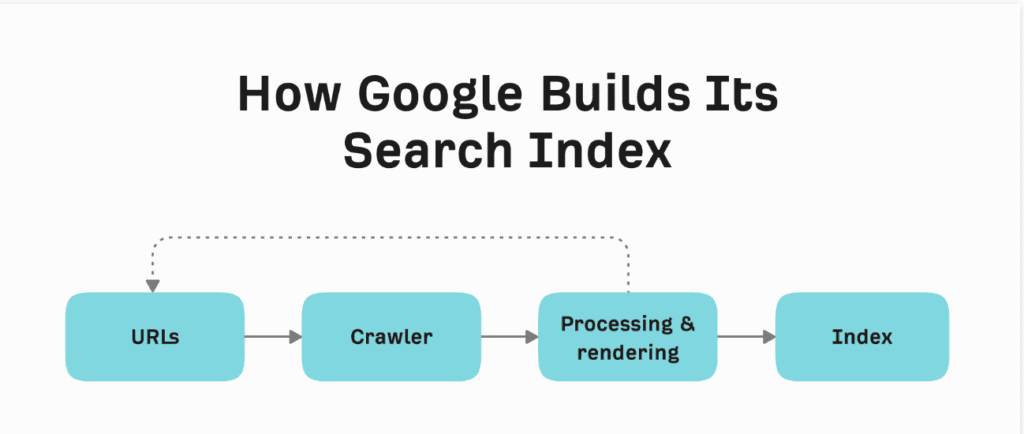
Let’s break it down step by step:
URLs:
Everything begins with a list of known URLs. Google discovers these in several ways, most commonly through:
-
Backlinks: Google already has an index containing hundreds of billions of web pages. When a new page is linked from an existing one, Google can follow that link and discover it.
-
Sitemaps: Website owners create sitemaps to help Google understand which pages and files are important. This acts as a guide to ensure all key content is crawled.
-
URL Submissions: Through Google Search Console, site owners can manually request Google to crawl and index specific URLs.
Crawling
Crawling is the first step in how search engines discover new content. It’s carried out by automated programs known as spiders or bots, which visit and download web pages from the internet.
Google’s crawler, called Googlebot, systematically scans known URLs to gather data about each page and detect new links that lead to other pages.
Processing and Rendering
Once a page is crawled, Google moves on to processing and rendering. This stage helps Google understand the structure and content of the page.
To do this, Google renders the page — essentially running its code to see how it appears and behaves for real users. During this process, Google extracts key details like text, images, metadata, and links to other pages.
Although the exact workings of this system remain a mystery known only to Google’s engineers, what matters most is that it helps Google store page content and discover new URLs for future crawling and indexing.
Indexing
After a page has been crawled and processed, its information is added to the search index — a massive digital library that powers every search result.
When users perform a search, they’re not scanning the live web — they’re searching through this index. That’s why being indexed by major search engines like Google and Bing is absolutely vital. If your pages aren’t indexed, users simply can’t find you.
Did You Know?: Google commands an astonishing 91.43% share of the global search market. This dominance means that being visible in Google’s index can drive far more traffic to your website than any other search engine.
Part 3: How Search Engines Rank Pages
Discovering, crawling, and indexing are just the beginning of the journey. Once a search engine has built its index, it needs to decide which pages deserve to appear first when a user types in a query. This is where search algorithms come into play.
What Are Search Algorithms?
Search algorithms are complex formulas and systems designed to match and rank the most relevant pages from the search index. These algorithms analyze hundreds of signals to determine which results best satisfy a user’s intent.
Google, in particular, relies on a combination of AI-driven systems and ranking factors that evolve continuously to provide more accurate and trustworthy results.
Key Google Ranking Factors
No one outside Google knows every ranking signal the company uses — and that’s intentional. However, over the years, SEO experts have identified several major factors that consistently influence rankings. Let’s look at some of the most important ones.
Backlinks
Backlinks are links from one website to another — and they remain one of Google’s strongest and most influential ranking factors.
In simple terms, a backlink acts like a vote of confidence. When other reputable sites link to your content, it signals to Google that your page is valuable and credible.
In fact, research involving over a billion web pages found a strong correlation between the number of unique linking domains and the amount of organic traffic a site receives. The more quality backlinks a page earns, the higher its potential to rank.
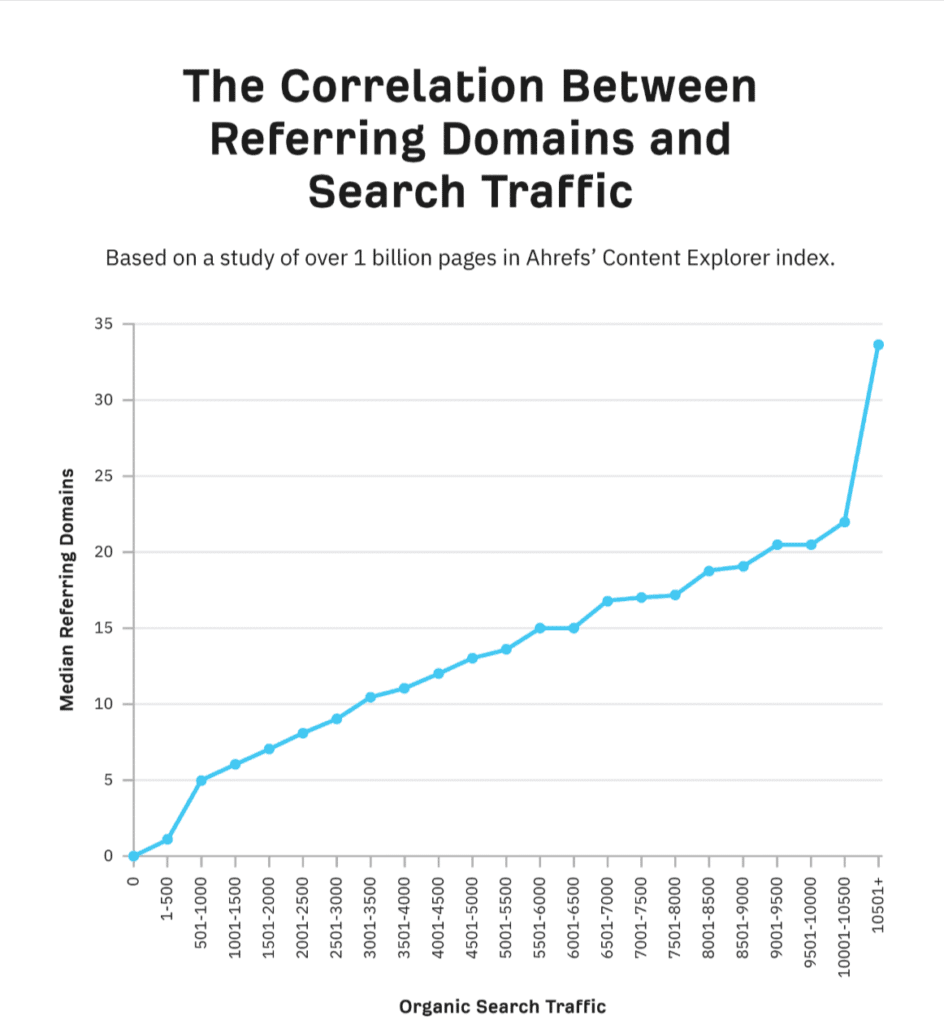
It’s not all about quantity, though. Quality matters too. Pages with a few high-quality backlinks often outrank those with many low-quality backlinks.
Relevance
Relevance refers to how closely a page’s content matches what a searcher is looking for. Google evaluates this in many ways.
At the most fundamental level, it looks for pages containing the same or related keywords as the user’s search query. But keyword matching is just the start — Google also analyzes context, search intent, and user behavior to refine its understanding.
For example, if people consistently click on a particular result and spend time engaging with it, Google interprets that as a sign of usefulness. Over time, such pages are more likely to appear higher in search results because they’ve proven valuable to users.
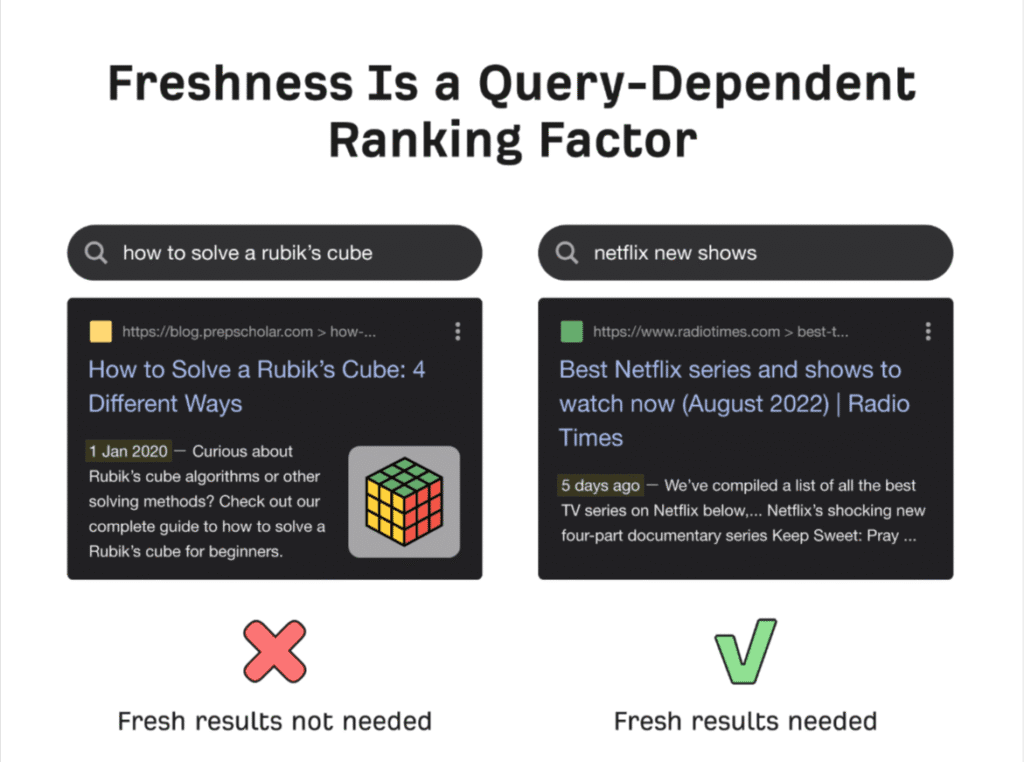
Page Speed
Page speed plays a crucial role in both desktop and mobile rankings. Google has confirmed that it’s a ranking factor — but it functions more as a negative signal than a positive one.
In other words, having a super-fast site won’t necessarily guarantee top rankings, but having a slow-loading website can definitely hold you back.
A sluggish page frustrates users, increases bounce rates, and signals to Google that the experience isn’t ideal. So while speed alone may not win you rankings, improving it can prevent your site from being penalized — and ensure visitors stay long enough to engage with your content.
Mobile-Friendliness
Mobile-friendliness has been an important ranking factor for both mobile and desktop searches since Google’s shift to mobile-first indexing in 2019.
This means Google primarily uses the mobile version of a website’s content for indexing and ranking. If your site doesn’t display properly or function smoothly on mobile devices, it can directly affect your visibility in search results.
A mobile-friendly website ensures that pages load quickly, text is readable without zooming, and navigation is effortless — all of which improve user experience and signal to Google that your site is built with modern browsing habits in mind.
Part 4: How Search Engines Personalize Results
Search engines, especially Google, tailor search results uniquely for each user. This personalization helps deliver results that best fit a person’s needs, preferences, and context. To do this, Google draws insights from several factors — including your location, language, and search history. Let’s explore how each one shapes what you see.
1. Location
Google uses your geographical location to provide results that make sense for where you are. For example, if you search for “Italian restaurant,” you’ll see nearby dining options instead of restaurants on another continent.
This is because Google understands local intent — it knows you’re looking for something accessible and relevant to your area, not something halfway across the globe.
2. Language
Language plays a key role in personalization. Google aims to show content that matches the language you speak and understand.
That’s why a user searching in Spanish will see Spanish results, while an English-speaking user will see English ones. When localized versions of content are available, Google prioritizes them to enhance the browsing experience and improve comprehension.
3. Search History
Google also personalizes search results based on your past behavior — such as your previous searches, sites you’ve visited, and even the places you’ve been.
This helps Google anticipate what you might find most relevant or interesting. While users can choose to opt out of this tracking, most people leave it enabled, allowing Google to refine results continuously for a smoother, more customized search experience.
Key Takeaways
-
A search engine is made up of two main components: an index and algorithms.
-
To build its index, it crawls known pages and follows links to discover new ones.
-
Search algorithms are designed to deliver the best, most relevant results for each query.
-
The quality of search results plays a vital role in building user trust and market share.
-
While Google’s exact ranking factors remain undisclosed, key influencers include backlinks, relevance, freshness, page speed, and mobile-friendliness.
-
Google also personalizes search results using your location, language, and search history to enhance user experience.
Conclusion: How Search Engines Work
Search engines are the silent architects of the digital world — constantly crawling, indexing, and ranking trillions of pages to bring order to the vast ocean of information online.
To master SEO, you must first understand how this invisible machinery works — from the moment a bot discovers your page, to how Google’s algorithms decide whether it deserves a place in the spotlight.
The magic of visibility lies in harmony — relevance, authority, and user experience working together like the rhythm of a well-tuned instrument. When your content truly serves people — answering their questions, loading fast, and shining with authenticity — search engines take notice.
So, as you step forward in your SEO journey, remember this:
you’re not just optimizing for algorithms — you’re writing for people, guiding them through the web’s endless maze, one meaningful search at a time.